OEE vs TEEP: everything to know about Key Performance Indicators in production
Understanding the nuances between these two indicators is crucial for professionals looking to analyze their production status in real time and implement continuous improvement strategies.
Introduction to Performance Indicators in industrial production
In the context of Industry 4.0 and industrial engineering, measuring the performance of production equipment is essential for optimizing processes, improving efficiency, and increasing competitiveness. Two major key performance indicators (KPIs) often used for this purpose are the Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) and the Total Effective Equipment Performance (TEEP).
What is OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) in production?
Definition of Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) is a key indicator that measures production efficiency by accounting for losses related to availability, performance, and quality. It is widely used in the industry to evaluate the operational efficiency of equipment or a production line.
Formula for OEE
OEE is calculated by multiplying three key factors:
![]()
- Availability: Ratio between actual operating time and planned operating time.
- Performance: Ratio between actual production speed and theoretical production speed.
- Quality: Ratio between the number of conforming pieces and the total number of pieces produced.
Learn more on OEE secondary KPIs
Example of OEE calculation
Suppose a machine is planned to operate for 8 hours (480 minutes). It experienced 30 minutes of unplanned downtime, thus operating for 450 minutes. The theoretical production speed is 100 pieces per hour, but it operates at an actual speed of 90 pieces per hour. Of the pieces produced, 95% are of acceptable quality.
Calculating OEE:
- Availability: 450/480 = 0.9375 = 93.75%
- Performance: 90/100 = 0.9 = 90%
- Quality: 95/100 = 0.95 = 95%

What is TEEP (Total Effective Equipment Performance) in production management?
Definition of Total Effective Equipment Performance (TEEP)
Total Effective Equipment Performance (TEEP) is a more comprehensive performance indicator that takes into account, in addition to the factors of OEE, the total available time, including periods not scheduled for production. It measures the actual efficiency of equipment utilization relative to their total capacity, offering a global view of performance in industrial production.
Formula for TEEP
TEEP is calculated by multiplying the Utilization Rate, performance and quality:
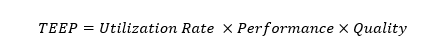
- Utilization Rate: Ratio between planned operating time and total available time
- Performance: Ratio between actual production speed and theoretical production speed.
- Quality: Ratio between the number of conforming pieces and the total number of pieces produced.
Learn more on TEEP secondary KPIs
Example of TEEP Calculation
Returning to the previous example. Suppose the total available time for the machine is 24 hours (1,440 minutes).
- Utilization Rate: 450/1,440 = 0.3333 = 33.33%
- Performance: 90/100 = 0.9 = 90%
- Quality: 95/100 = 0.95 = 95%
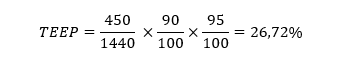
Differences between OEE and TEEP in industrial production
- OEE: Focuses on periods where production is planned. It excludes scheduled downtimes like preventive maintenance or breaks.
- TEEP: Encompasses the total possible utilization of the equipment, including periods not scheduled for production. It offers a more holistic view of equipment efficiency.
Practical application
- OEE: Ideal for analyzing operational efficiency during planned production periods. Used to identify losses related to performance, availability, and quality.
- TEEP: Useful for evaluating the overall improvement potential, including increasing planned production hours. It helps identify underutilized operational opportunities.
Advantages of OEE in optimizing production
- Detailed Analysis: Offers a precise view of operational losses during production periods.
- Targeted Improvement: Allows for specifically targeting issues of availability, performance, or quality.
- Comparability: Facilitates comparison between different machines or production lines during the same time frames.
Advantages of TEEP for effective resource management
- Global View: Provides a comprehensive perspective on the efficiency of equipment usage over the entire available time.
- Resource Optimization: Identifies possibilities to increase production by optimizing operating schedules.
- Strategic Decisions: Assists in long-term planning and capacity management in industrial production.
When to use OEE?
- Operational Analysis: When the goal is to improve efficiency during planned production periods.
- Problem Solving: To identify specific causes of losses and implement targeted corrective actions.
- Daily Monitoring: Useful for regular monitoring of machine or production line performance.
When to use TEEP?
- Strategic Planning: When evaluating overall production capacity and asset utilization.
- Schedule Optimization: To decide on extending production hours or adjusting maintenance schedules.
- Investment Management: Helps determine if new equipment is necessary or if better utilization of existing equipment is possible.
Integration with international standards (OEE and TEEP)
In practice, OEE and TEEP are widely recognized international standards:
- OEE: Measures efficiency during planned production hours.
- TEEP: Evaluates total efficiency by including all available time.
These international standards offer proven and widely accepted methodologies, facilitating the standardization of performance analyses on a global scale.
Conclusion
The choice between OEE and TEEP depends on the specific objectives of the performance analysis. OEE is ideal for a detailed analysis during planned production hours, allowing for the identification and correction of operational inefficiencies. TEEP provides an overview of equipment utilization, helping to identify strategic opportunities for improvement and resource optimization.
By understanding the nuances between these two key performance indicators, professionals can select the most relevant KPI for their needs, optimize their production processes, and make informed decisions to enhance the overall efficiency of their enterprise.
